Osteochondrosis generally refers to degenerative changes of any articular cartilage. Therefore, this pathological condition can occur in all joints of the musculoskeletal system. However, the most pronounced symptoms, for example headaches and headaches, as well as heart pain, are recorded in the case of cervical osteochondrosis, ie damage to the cartilage tissue between the vertebrae of the cervicobrachial spine.
According to WHO statistics, about 60% of Europeans suffer from osteochondrosis to one degree or another. In men, the disease manifests itself approximately 10 years earlier than in women. Older people have been experiencing symptoms for about 45 years. The female half is 55-60 years old. At the same time, experts are ringing the alarm for the ongoing rejuvenation of this disease. If you do not take timely measures, then the number of 30-year-old patients with osteochondrosis will literally increase significantly in the next decade.
Causes of osteochondrosis

Dystrophic changes in the pulp occur for a variety of reasons. Natural aging of cartilage tissue should be put in the first place, which is, alas, an objective and irresistible circumstance. However, as mentioned above, this disease is getting younger, which is no longer associated with aging, but with other reasons.
In young patients, the disease occurs as a result of metabolic disorders associated, as a rule, with improper diet. The abundance of fat and low content of vitamins in foods are the reason that cartilage begins to literally "starve" and reach a state of dystrophy.
Another provocative factor is physical inactivity. Read the forums where people who have encountered this disease communicate and you will see that most of them are still relatively young residents of mega cities, who are generally engaged in mental work that involves long sitting. Low motor activity of the cervical vertebrae leads to loss of cartilage elasticity on the intervertebral discs.
As a result of poor nutrition and related metabolic disorders, as well as due to physical inactivity, the pulp begins to degenerate, becoming denser. In the later stages of osteochondrosis, a complication occurs which is manifested by replacement of the cartilaginous tissue of the bones and thickening of the intervertebral discs. This leads to compression of the nerve and blood vessel roots located here. The involvement of the elements of the nervous and vascular system in the pathological process determines the specific course of osteochondrosis.
Disease specificity
The difficulty in dealing with this disease lies in the delayed diagnosis, which is explained by masking osteochondrosis under other pathologies. People lack precious time and do not treat this pathology because they are not aware of its presence. And patients can't be blamed for that. If the pressure jumps, then we treat hypertension. A stabbed heart - let's go to cardiology. The head hurts regularly and now a person cannot fall asleep without ibuprofen or analgin. It doesn’t even occur to us that we need to visit a neuropathologist.
Meanwhile, just a few visits to a specialist in this profile will allow you to begin the process of restoring the cartilage of each cervical spine, which will gradually eliminate both false hypertension and suspected angina pectoris, and persistent headaches, and other symptoms associated with cervicalthe shoulder area of the spine, it seems to us, is not connected.Timely detection of pathology prevents further pulp dystrophy and allows you to treat osteochondrosis at home and on an outpatient basis - without hospitalization. Unfortunately, the lion's share of patients turn to a neuropathologist already with sufficiently severe lesions of the intervertebral discs - when the neck begins to ache unbearably.
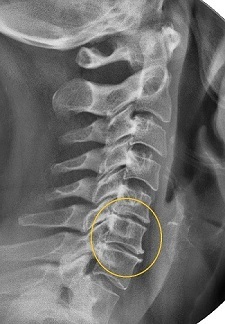
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosing osteochondrosis is a complex job. Research can take a long time, but the costs are justified, as early treatment of this disease avoids the worst-case scenario - surgery to replace the ossified intervertebral disc, during which compressed nerve roots are released and full-function implants or simple height compensators are installed. removed spine element. The orthopedist determines what solution is needed for a particular patient after a comprehensive diagnosis.
Since the disease, as mentioned above, is masked, you must first be sure that the symptoms are not related to problems in other organs. For example, in the case of heart pain, you must undergo a cardiac examination and confirm the absence of heart disease. A comprehensive diagnosis will allow not only to confirm the suspicion of osteochondrosis, but also to find out the general condition of the body along the way.
The final diagnosis is made based on the results of X-ray examination of the cervicobrachial spine in frontal and lateral projections. A more informative method is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It allows you to more accurately determine the location of dystrophic changes. Thanks to this, the doctor gets the opportunity to prescribe literally a point treatment.
Treatment with folk remedies at home
The advantage of osteochondrosis, if this word is used at all in this case, is that the patient can be treated at home, without mandatory hospitalization. The course of treatment includes taking special medications and performing exercises from the exercise complex.
Drugs (their types) used to treat osteochondrosis at home are presented in the following table.
| Painkillers | In most cases these are tablets, sometimes capsules. These remedies are intended to relieve pain in the cervical spine. |
| Anti-inflammatory | Hormonal drugs that stop the inflammatory process resulting from changes in the intervertebral cartilage. It also relieves pain. |
| Chondroprotectors | Medicines that contain components to restore cartilage tissue, such as hyaluronic acid. Designed for long-term use. |
| Muscle Relaxants | A means of relaxing muscle tension. These medications are only taken under the supervision of the treating physician. Limited use due to a large list of contraindications. |
| External | Ointments, gels and so on. They are used anti-inflammatory, analgesic and warming. Before using these funds, you should consult an expert. |
| Vitamins | Preparations with vitamins that improve the conduction of nerve fibers and the general functioning of the peripheral nervous system. These are B vitamins, as well as A and C. In some cases, vitamin D is prescribed. |
It should be understood thatour list of drug types does not provide a basis for self-medication. Only a certified neurologist can prescribe a specific agent with an indication of dosage and taking into account the pathogenesis in each individual case. Reckless adherence to television commercials that "recommend" the best drugs for osteochondrosis is not burdened with a cure for this disease, but, on the contrary, worsening of the situation. BE CAREFUL!
Injection therapy
Injecting drugs are used to treat osteochondrosis, in addition to taking pills and applying ointments. There is a wide range of injectable medications. Treatment courses include all types of injections, which include the following: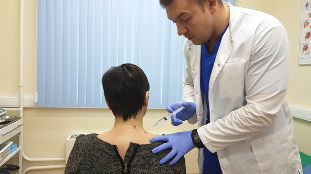
- subcutaneous;
- intramuscularly;
- intravenously;
- epidurals.
Injections are more effective compared to medications taken orally and all types of folk remedies. Blood flow quickly brings the remedy to the sore spot, which explains the quick healing effect. And, for example, with an epidural injection, the drugs are injected directly into the spinal cord and begin to act immediately.
Vitamins and other supportive drugs are usually injected subcutaneously. Anti-inflammatory drugs and chondroprotectors are injected intramuscularly. For example,anti-inflammatory drug injections, which are so popular among patients, are injected into muscle tissue. Drugs that speed up cerebral circulation are given intravenously. This is necessary in the case of overgrown intervertebral discs that squeeze blood vessels, through which the blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the brain. Epidural injections are performed with the goal of blocking strong feelings of pain when other methods of pain relief are ineffective. With this injection, the needle passes between the spinal processes and delivers the anesthetic directly to the spinal cord. This procedure is performed only by a trained professional anesthesiologist.
Injections are fully effective only under the condition of regular exercise in medical gymnastics. That is, the administration of drugs alone is not sufficient to completely cure osteochondrosis. Only in combination with exercise therapy is it possible to alleviate the symptoms of the disease, and in the future to restore the affected cartilage tissue.
What to do during deterioration?
Although osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is chronic and more or less unnoticeable over an extended period of time, sometimes patients face exacerbations. They occur at different intervals in each patient and can occur unpredictably. During these periods, it is important to take timely measures to prevent a significant deterioration of the condition.
Provocateurs of deterioration
Worsening of osteochondrosis, as with any other disease, does not occur, as they say, suddenly. Usually acute conditions are caused by the following factors:
- stress;
- non-professional massage;
- weather phenomena;
- visit to the thermal bath (sauna);
- excessive physical activity after prolonged physical inactivity.
In women, osteochondrosis often worsens during menstruation. Alcohol abuse is also a powerful provocative factor.
Symptoms of worsening
Symptomatology of worsening osteochondrosis in each patient is manifested differently and is determined by the general clinical picture of the pathogenesis. For example,cervical and headache in acute conditions are noticed by all patients, and the loss of sensitivity to facial stiffness during exacerbation is not felt by all, but, nevertheless, it happens quite often. And, of course, during this period, the symptoms of those diseases under which osteochondrosis is masked worsen. These are heart pain, dizziness, tinnitus, hot flashes and so on. Particularly dangerous are the exacerbations during which inflammation of the cervical spine occurs.
Deterioration relief measures
In the period of severe osteochondrosis, it is necessary, first of all, to consult your doctor. It is not necessary to ignore this rule, because being late in this matter can do a disservice. The neurologist will assess the patient's condition and recommend steps for an effective and, most importantly, safe way out of the crisis.
Injections of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs are usually prescribed during acute conditions with osteochondrosis. But gymnastics must be stopped during that period. On the contrary, the patient must be calm. It is unacceptable to squeeze the neck - it can make the condition worse. It is desirable to transfer the aggravation to a lying position and at the same time fix the head, placing a roller or at least a rolled sheet under it.An important place in reducing the frequency of deterioration is played by their prevention, which comes down to maintaining a proper motor regime in everyday life.A patient with osteochondrosis should monitor posture, keep his head upright, avoid sudden movements. In humid and cold weather it is necessary to protect the cervical vertebrae from hypothermia. And, of course, you shouldn’t forget about medical gymnastics for a minute - you should do it regularly. This is the key to the course of osteochondrosis without worsening.
2nd degree disease
Neuropathologists distinguish 3 degrees of osteochondrosis - first, second and third. In the lion's share of patients, the disease is recorded in the second stage. This is due to the following points. Grade 1 disease is characterized by the appearance of short-term pain in the neck, which resembles electrical discharge. In the initial stage, the fibrous ring, which holds the central part of the intervertebral disc, begins to collapse. The guideline for the diagnosis of grade 1 osteochondrosis is pupil dilation, which is not associated with other phenomena in the body.
The number of patients with grade 1 osteochondrosis is not too large. The disease is transient in this phase and is either removed (with timely treatment), or quickly passes into the second phase - if the moment is missed. The situation is similar with the number of patients with osteochondrosis of the 3rd degree. It's also small. This is due to the fact that most often doctors manage to start timely treatment and prevent the transition of pathology from the second to the third stage. The disease of this degree is characterized by symptoms such as acute neck pain, which does not subside even after taking pain medication, partial loss of control of the upper limbs, constant dizziness and often fainting. Grade 3 osteochondrosis is usually treated with surgery, as drug therapy is often ineffective.
Due to the fact that most patients suffer from grade 2 osteochondrosis, this form of the disease is of the greatest interest from a clinical point of view, and it is precisely in the treatment of the disease that the greatest experience has been gained. According to statistics, the share of patients with stage II osteochondrosis among all patients with this pathology is about 75%.
The specificity of this form of the disease is its chronic course with short periods of worsening.The second stage differs from the first by continuously reducing the space between the vertebrae. That is, the intervertebral disc has not yet collapsed, as in the case of the third phase, but it becomes significantly thinner, which leads to constriction of the nerve roots and causes all the classic symptoms of osteochondrosis.
Since pathology of the II degree is the most widespread, speaking about the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis in general, they imply the implementation of therapeutic measures in connection with this particular form of the disease. And they, we repeat, include drug therapy and physiotherapy exercises. Properly performed treatment allows you to remove the disease and prevent its transition to the third phase with the almost inevitable surgery to replace the intervertebral discs.
Main symptoms and proper treatment
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is difficult to diagnose as a degenerative lesion of the intervertebral discs. It is most commonly encountered by people aged 45-50, but in recent years the pathology has “rejuvenated” and now neuropathologists often see patients in their 30s.
The difficulty of detecting osteochondrosis is explained by the "simulating" nature of the course of the disease - when it is disguised in other pathologies. The cause of the disease is a deterioration in the elasticity of cartilage tissue, which creates a damping pulp between the vertebrae. The cartilage becomes thinner and denser. As a result, the nerve roots are compressed (so-called radicular injury), which leads to the following symptoms:
- headaches and heart pain;
- high blood pressure;
- decreased sensitivity of the facial area (to numbness);
- partial paresis of the upper limbs.
All these symptoms are certainly accompanied by neck pain. Often these pains are mild and do not force the patient to take painkillers. Ignoring the slight pain in the neck, the patient does not sound the alarm due to osteochondrosis, but tries to treat other pathologies, for example, angina pectoris or hypertension, which are most likely absent.
Treatment Methods
According to modern approaches, osteochondrosis takes place in waves. It initially manifests itself in the form of exacerbation (acute period). Then the symptomatology weakens and the subacute period occurs. The third stage is remission, whose condition continues until the next deterioration. The task of treating osteochondrosis is to quickly stop the acute phase, alleviate the patient's condition in the subacute period and ensure long-term remission.
During the acute and subacute phases, the patient takes painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. In these stages, an effective solution is to use a Shants gauze collar, which gives the head a position where the neck muscles relax, which removes pain. During the period of remission, treatment with chondroprotectors that improve the quality of cartilage tissue and a series of exercises for physical exercises is indicated. Gymnastics is even more important than hyaluronic acid injections because healthy physical activity naturally stimulates the formation of collagen fibers in cartilage.
Cervico-thoracic type of pathology
Strictly speaking, cervical and thoracic osteochondrosis are two different forms of the disease. However, they are often combined. This is due to the fact that the cervical and thoracic spines are closed to each other, which connects these two types of pathology of the intervertebral discs. That is, with dystrophic changes in the cervical vertebrae, virtually the same violations are observed in the thoracic region. Therefore, these two forms of the disease are combined, especially since their symptoms are very similar to each other. The main symptom is pain. In cervical osteochondrosis, the pain is localized in the neck, in the case of a cervicothoracic lesion they are accompanied by pain in the sternum.
Common symptoms include the following:
- facial numbness;
- headache and heartache;
- blood pressure instability;
- loud tinnitus.
In case of damage to the thoracic spine, the list is supplemented by impaired coordination of movements, activation of arthrosis of the shoulder joints, numbness of the hands.
Treatment of cervicothoracic spine
Treatment is prescribed after a thorough diagnosis using X-ray or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The treatment of osteochondrosis is complex - drugs and physiotherapy. Drug therapy involves taking anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs.An important part of treatment is the use of chondroprotectors that directly regenerate cartilage tissue in the intervertebral space. Physiotherapy measures include dressings and the use of all types of fats, as well as physiotherapy exercises.
If osteochondrosis is detected in the thoracic spine, professional massage is indicated. The effects of massage trigger the natural processes of cartilage tissue regeneration. Massage is more effective in removing thoracic spine disease than gymnastics, because the spine is not flexible at this point, so it is not always possible to ensure a normal range of motion for individual vertebrae when performing exercises. On the other hand, a massage therapist can accurately affect a diseased intervertebral disc. Only you need to contact a spine massage specialist who has the appropriate certificate. Also, a massage therapist must be licensed.
Timely measures to remove cervicothoracic osteochondrosis will make it possible to avoid surgery to replace the destroyed intervertebral disc with an endoprosthesis. Early diagnosis of pathology and disciplines in outpatient treatment with drugs and folk remedies will save you money. If you have the slightest suspicion of osteochondrosis, consult a neurologist. But better. . .
Be sure to consult your doctor before treating the disease. This will help you consider individual tolerance, confirm the diagnosis, ensure the correctness of treatment, and rule out negative drug interactions. If you use prescriptions without consulting a doctor, it is entirely at your own risk. All information is provided for informational purposes only and is not medical assistance. You are solely responsible for the application.



































