All synovial joints are subjected to degenerative diseases – arthritis, but some more, some less. Most often osteoarthritis affects the knee and hip joints because they are exposed to significant loads, and knee joints – and even injuries. If the arthritis is localized the knees, diagnosed gonarthrosis (osteoarthritis deformans of the knee joint). Knee osteoarthritis – a disease that often leads to temporary disability and disability. What is osteoarthritis of the knee joint, for some reason develops and how this is manifested the disease, how to treat it – the topic of this article.
A bit of terminology
Osteoarthritis – non-inflammatory articular disease that starts with degenerative processes in the articular cartilage, then the process involves the articular area mating bone, synovium, soft muscles, which support joints. Another name of this disease is osteoarthritis, it indicates that the pathological processes occurring in bone tissue.
To Refine the localization to a disease name add the name of the body: osteoarthritis of knee, osteoarthritis of the ankle joint. Because at a late stage of the regional expansion of the articular sites lead to severe deformation of the body, osteoarthritis of the knee joint and other articular joints is called deforming, abbreviated as DOA. The diagnosis of DOA means the same as osteoarthritis.
What is osteoarthritis and how it is called? Quite often in the Internet you can find the phrase gonarthrosis of the knee, osteoarthritis of the hip joint. If the first definition is a tautology, the second is a mixture of the names of two different joint diseases. The fact that for convenience, denote the most common types of arthritis use of the name, which refers to localization. So, the first part of a compound word "gonarthrosis" to go to the Greek word, which means "knee." That is, the gonarthrosis is osteoarthritis of the knee, can also be used as the name DOA of the knee joint, knee osteoarthritis. And the axis titles gonarthrosis of the knee joint and the like are redundant.
Knee anatomy
In the literature we can also find mention of femoro osteoarthritis-patellar joint or patellofemoral syndrome. To understand what it is, you need to get acquainted with the anatomy of the knee joint. This is a condylar joint:
- the articular surface of the femur is a convex head;
- the tibia is hollow.
In addition to large tubular bones in the formation of the knee joint takes part a small sesamoid bone known as the kneecap or patella. The rear surface of its upper edge articulates with the femur. Patella in Latin is called the patella and the femoral bone – femara. That is, if translated into Russian word femoropatellar, you get a femoro-patellar. This is not a standalone joint, and an integral part of the complex knee joint. Holds the patella in the correct position system communication, but sometimes it moves due to injury or initially has the configuration to cause instability.
Displacement, instability of the patella – the main factors leading to the development of the so-called patellofemoral osteoarthritis. The causes also include traumatic damage to the cartilage of the patella at blows, falling. Experts usually use the term patellofemoral pain syndrome, as the mechanism of development and clinical picture of this pathology is different from the classical, typical for osteoarthritis. These diseases are treatable, since thinning of the cartilage (chondromalacia a) there is only 3 stages, the prognosis is very favorable. Ale without proper treatment this disease go in gonarthrosis.
The causes of the disease
What is osteoarthritis of the knee and what causes it cause? One we have already mentioned – injury and instability of the patella, running patellofemoral syndrome (physicians often view it as pietros).
The causes of osteoarthritis of the knee include:
- the inherent weakness m Azovo connection binding device stabilizing a knee joint;
- vascular disease of the lower extremities (varicose veins, thrombophlebitis), which disturbed blood supply to the knee;
- protracted inflammatory processes in the joint cavity and periarticular tissues;
- endocrine diseases, especially diabetes;
- injuries of the lower extremities.
Arthrosis of the knee, threatens people diagnosed with DOA ankle, the hip, flat feet. With the defeat of the ankle or hip joints, a violation of the support function of the foot increases the load on the knees. With age, the incidence of osteoarthritis of the knee is increasing. POV this is due to the slowdown of metabolic processes and regeneration processes and blood circulation disorders, natural wear of cartilage, changes in hormonal levels.
Gonarthrosis at a young age often develops in persons with genetic predisposition, genetic defects of connective tissue. He is also prone to athletes and people engaged in heavy physical work load on the legs. Much harm knee joints weight.
Symptoms
If you have arthritis of any localization symptoms gradually increase from stage to stage. 1 stages of osteoarthritis, the patient experiences discomfort:
- legs get tired quickly;
- in the beginning of the movement there is a short pain, a feeling of tightness, stiffness, but about half an hour these symptoms disappear;
- pain may recover after prolonged stress, but to go after the rest.
2 stage small enough load to cause pain, and requires longer rest to pass. Since this stage is often inflamed synovium to mechanical joining of inflammatory pain that occur at rest. For synovitis characterized by the increase of the knee due to accumulation of inflammatory effusion in the joint cavity, the skin often become red, hot to the touch.
If early contractures (limitation of joint mobility) are mainly related to pain during movement, according as the disease progresses, knee articulation, contractures become resistant. Grow osteophytes that prevent the movements become shorter and lose their elasticity of the ligaments, weakens the muscles of the soft, reduced production of intra-articular lubricant – synovial fluid. 3 stage range of motion is greatly reduced, some patients may only rocking motion in the knee. Finally, at a later stage the joint is deformed bone growths, leg bent at the knee (X-shaped or O-shaped deformation).
What is osteoarthritis of the knee and what symptoms to distinguish it from patellofemoral syndrome? For the last characteristic:
- pain localized to the anterior aspect of the knee that is felt usually while running, aggravated by squats, lifting from the chair, walking the stairs;
- swelling in the region of the patella;
- limp stroke;
- it clicks during movement, and clicks and pain do not occur simultaneously.
Swelling of the knee, gait changes, pain is characteristic of osteoarthritis, but the pain is felt deep in the joint, often suffers from its inner side. Movement often accompanied by pain and crepitus. To pinpoint the localization process, the necessary functional tests and x-rays.
Diagnostic methods
The diagnosis is DOA put after a comprehensive examination of the patient. First, the doctor listens to complaints, is studying the history, examines feet, palpated joints, performs passive movements and ask the patient to perform active range. Gonarthrosis are one-sided and two-sided. In unilateral lesions the healthy limb compared to patient. Assess range of motion, m Yazov force, measure the girth of the thighs and shins, feet length. Because the osteoarthritis is accompanied by atrophy of muscles and ligaments, the injured leg has reduced and shortened.
After physical examination and laboratory assign hardware:
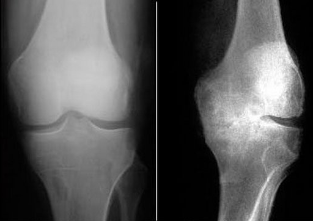
- the main method of diagnosing osteoarthritis x – ray image is at least 2 projections;
- CT scan – a type of x-ray examination, during which gives a layered image of a joint;
- assess the condition of the cartilage, soft tissue, the volume of synovial fluid allows ultrasound;
- a highly informative method of diagnosis – MRI;
- the tests are assigned to distinguish osteoarthritis from arthritis and other inflammatory diseases.
In the diagnosis and determining the extent of osteoarthritis in knee joints based on x-ray data.
- Minor, usually irregular narrowing of the joint space, osteophytes initial in the form of small aggravations along the edges of the articular sites.
- The articular narrowing of the lumen by 50% or more, multiple large osteophytes, compaction of bone tissue (osteosclerosis) in the places of greatest load. On the background of foci of osteosclerosis may be observed enlightenment testopodobnymi cavity.
- The almost complete absence of the articular gap, pronounced osteosclerosis, coarse osteophytes, deformation of the articular surfaces of bones, smoothing its relief, the curvature of the axis of the limb.
Treatment
Next question: what is arthrosis of the knee and how to deal with it? Methods of treatment of this disease is diverse, it is extremely important integrated approach, a combination of drug and non-drug therapy. Treatment should start with limiting the load on the knees. It is necessary to refuse from running, jumping, lifting, patients who are overweight should lose weight.
Whose soft muscle is weakened due to a sedentary lifestyle, you need to move more, but not to overload the knee. Shoes should be comfortable, when walking it is recommended to use a cane, also an orthopedist can pick up the knee, orthosis and other devices for unloading and stabilization of the joint. Definitely need to stick to a diet.
Medication

How to treat arthritis if it is accompanied by pain? Most often they are cropped using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that are given orally and used in the form of ointments, gels. Additionally prescribe irritating ointment. During intense inflammatory process can be shown injection into the joint of hormonal drugs in combination with local anesthetics. But this treatment only relieves the symptoms, it is conducted short courses, according to testimony.
At the 1-2 stages of symptomatic treatment necessarily must be combined with long-term administration of chondroprotectors. These drugs slow the breakdown of cartilage, and at an early stage even contribute to its recovery. Well relieve pain and restore mobility intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid.
Of drugs in osteoarthritis may also be administered vasodilators and drugs to improve microcirculation, their readings are in violation of the blood supply to the joint. To remove m Azov spasms help muscle relaxants. Specific treatment for osteoarthritis along with cartilage protectors is a drug which neutralizes the activity of a protein that destroys cartilage.
Non-drug treatment
Indicated for osteoarthritis of the knee and non-drug treatment. The methods of non-pharmacological treatments include:
- physiotherapy electrophoresis, ultrasound, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, shock wave therapy, ultraviolet irradiation, and others;
- application of paraffin, ozokerite;
- compresses with Dimexidum, medical bile, bischofite;
- massage with the influence not primarily on the joint itself and surrounding soft connection;
- manual therapy – stretching or mild reduction of the joint;
- Physical therapy, therapeutic gymnastics. To master the exercises in this training video, descriptions of complexes with a photo, but it is better to start exercising under the supervision of an instructor.
In a number of clinics to be tested an innovative method of treatment – stem cell therapy. It allows you to restore cartilage tissue without resorting to surgery.
1 stage of gonarthrosis are shown only conservative treatment, starting with 2 may be performed surgery. Most advanced surgery for osteoarthritis:
- arthroscopic of debridment – removal of osteophytes and necrotic areas of cartilage through a small incision;
- arthroscopic chondroplasty – fix articular cartilage;
- arthroplasty – joint replacement artificial.
The first two operations are usually carried out in 2 stages, give temporary effect for 1-2 years. The endoprosthesis shown in 3 stages of osteoarthritis of the knee, is the only way to avoid disability. Implants last 15-20 years, and then have a second operation.
Gonarthrosis or arthrosis of the knee to enter the three most common types of arthritis. Knee pain can point not only to the development of osteoarthritis, but the damage to the ligaments and menisci, arthritis and several other diseases. Therefore, the appearance of anxiety symptoms you need to pay to the doctor and get tested.
Most often osteoarthritis of the knee progresses slowly from the first symptoms to complete loss of function of a joint can take a couple of decades. Completely cure gonarthrosis impossible, but if you start treatment at an early stage is more likely to slow down its development and delay the last stage that lead to disability.



































